1、概况
外围买球app十大平台官网宇航推进系自成立以来,为我国航天推进事业培养了大批优秀人才,仅从1988年到2011年已培养本科毕业生约810名, 硕士生308名, 博士生148名, 留学生36名。目前每年招收本科生60名左右,硕士生45名左右,博士生15名左右, 留学生5名左右。
目前宇航推进系所属一级学科“航空宇航科学与技术”和二级学科“航空宇航推进理论与工程”,自建立以来,在历次全国评估中均排名第一,航空宇航科学与技术一级学科被评为国家重点学科。首批进入国家2011计划,宇航推进系代表北航主持宇航科学与技术协同创新中心“能源与动力平台”的建设工作,圆满完成平台建设工作。2007年成立了“电推进技术”特色学科。2009年获批建设国家及北京市精品课“火箭发动机专业综合实验”。先后获评校优博6人次、全国优博提名、北京市优博各1次。
科学研究涵盖液体火箭发动机、固体火箭发动机、电推进技术、固液火箭发动机、冲压发动机等类型。取得一批国际、国内领先、先进的研究成果,多次获得国家发明二、三等奖及其它部委级科技进步和发明一、二、三等奖等一系列科技奖,教师人平均科研经费超过100万。
宇航推进系与中国航天科技集团有限公司北京11所联合申报获批了“低温液体推进技术”重点实验室;“航天器仿真优化与动态模拟”教育部重点实验室正式挂牌运行,依托实验室建设大力发展航天器设计优化及动态模拟技术研究工作,宇航推进系参与承担了大量的建设和运行工作。2012年在沙河新校区落成6000余平米新的现代化航天推进实验室和真空羽流实验室,恢复和新建一批高水平的研究实验系统。建成的宇航推进仿真中心具有100万亿次的仿真能力。
积极开展国际国内合作交流。同美国、俄罗斯、欧洲的著名高校航天相关院系和院所机构保持长期科研协作关系和人员学术交流。2007年主办空间推进国际学术会议,有来自美、俄、欧、日等国的29位外国著名专家出席该会议。同俄罗斯协作建成了国际一流水平的真空羽流效应实验系统。
2、历史沿革
1956年在国家发展火箭技术的大背景下,北京航空航天大学(原北京航空学院)成立了我国第一个“火箭发动机教研室(307教研室)”,由两弹一星元勋屠守锷负责,北航前任校长曹传钧担任首任主任。1958年后分别成立“液体火箭发动机设计教研室(603教研室)、固体火箭发动机设计教研室(605教研室)及火箭发动机研究室(第九研究室)”。同年成功发射我国及亚洲第一、两种二级探空火箭“北京二号”(注:第一种:一级为固体火箭发动机,二级为液体火箭发动机;第二种:两级都是固体火箭发动机)。
1960年10月历时一年零一个月由4个15吨推力室组成的60吨级液氧/煤油液体火箭发动机实验台在北京西山基本建成(15吨级进行了初步热试车),时任北京市市长万里、教育部部长杨秀峰、国防科委副主任钟赤兵等亲临实验现场参观,并得到钱学森等领导和专家的关注。
1970年院系调整时并入航空发动机系(四系)更名为“403教研室”,1988年新的外围买球app十大平台官网成立后于2006年又更名为宇航推进系至今。
由于历史原因,并入四系的403教研室只保留了与航空相关的固体火箭发动机专业,液体火箭发动机专业被一度放弃。这时的本科生人数每届约20人,隔年招生。
1977年与胜利油田共同研制地震火箭用于油田勘探,经过4年试验,于1981年研制成功,获国家发明三等奖。
1988年“403教研室”并入新成立的外围买球app十大平台官网后,通过恢复、建设、发展三个阶段(每个阶段约5年),使403教研室得到快速发展。1989年起恢复每年招生。
1990年恢复招收液体火箭发动机专业本科生,当年招生13人。
1991年宇航推进系派代表团出访俄罗斯莫斯科航空学院,引进小推力气氧-酒精液体火箭发动机实验台;1993年,又从莫斯科航空学院引进气动谐振点火实验台、泵台、减压器等,初步建成了液体火箭发动机实验体系,有力地配合了液体火箭发动机专业的建设。
固体火箭发动机专业方面,重点发展了固体火箭发动机CAD技术和固体缓冲火箭技术。1994年,为了拓展固体火箭发动机的应用领域,学校决定从俄罗斯国立波罗的海技术大学引进大尺寸气动激光器,该激光器是利用固体火箭推进剂泵浦能量的CO2气动激光,最高功率可达10kW以上。

气动激光打靶 地震火箭发明奖获奖证书
在特种推进方面,1997年通过“211”项目建成电火箭实验系统。2001年起在“863”项目的支持下,开展超燃冲压发动机、激光推进、核推进、爆震发动机等相关研究。
3、学科建设
宇航推进系所属“航空宇航科学与技术”一级学科,国内最早拥有该一级学科博士学位授予权。在2007年1月国家重点学科考核评估中被认定为国家重点一级学科,一直在全国排名第一。宇航推进系所属二级学科为“航空宇航推进理论与工程”,该学科1988年被国家教委评为国家重点二级学科,在历次教育部组织的学科评比中,始终排名第一,拥有博士、硕士学位授予权。宇航推进系于2007年获批建设国防紧缺二级学科“电推进技术”。宇航推进系是一个综合性很强的工程技术性学科,涉及机械、燃烧、流动、传热、等离子体物理、材料等学科;研究涉及试验、仿真计算、优化设计、测控、信息处理、电源等众多相关领域。
4、师资队伍
现有在编教师共44名, 拥有教授17名, 副教授23名, 其中包括国家级领军人才3人,国家级青年人才6人, 享受国务院政府特殊津贴专家2名, 新世纪人才1名, 绝大多数教师拥有出国研究经历,98%以上教师拥有博士学位。
5、教学工作
本科专业名称“飞行器动力工程(航天)”学制四年,培养目标是:培养面向未来发展, 富有创新潜质,具备团队精神,善于学习实践的高层次高素质人才。基本要求:掌握本专业必需的数学、物理等自然科学基础知识,掌握工程力学、机械设计、机械制造、电工电子、计算机应用等现代工程技术基础知识。主要专业基础课包括工程热力学、工程流体力学、气体动力学、传热学等。主干专业课包括火箭发动机原理(含固发原理、液发原理、液发系统原理、涡轮泵原理),火箭发动机设计(含固发设计、液发推力室设计、液发系统设计、涡轮泵设计)和火箭发动机专业综合实验等,专业综合实验课为国家和北京市精品课程。学科特点是综合性和工程性强,直接面向航天推进产品的设计与试验。设置生产实习、热工综合实验、专业课程设计、专业综合实验、毕业设计等实验实践环节。大学生科研训练参与人数多、规模大、投入高、持续时间长,显著提高了学生培养质量,得到广泛好评,如北航一号、二号、三号、四号等的成功发射。建立了完整、先进、规范的教学实验室和设备条件,包括演示性实验、引导性实验和自主性实验。
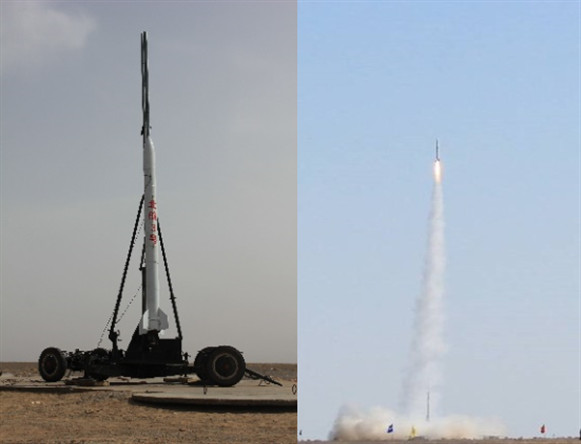

北航3号整装待发 发射升空
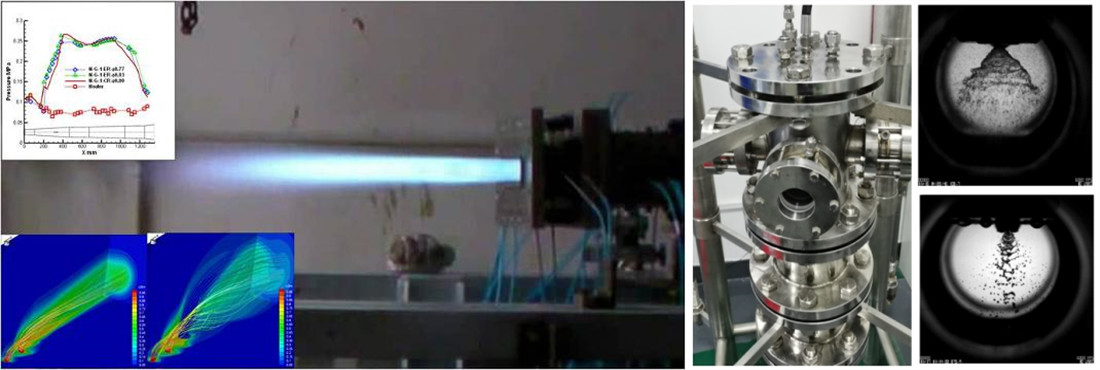
超燃冲压发动机试验 推进剂雾化试验
电推进试验 空间姿轨控发动机
6、科研工作
近年来宇航推进系面向国家重大战略需求和国际学术前沿,围绕真空羽流效应、可重复使用火箭发动机、固体火箭发动机、固液火箭发动机、姿轨控发动机及动力系统、电推进、超燃冲压及组合循环发动机、空间能源开发与利用、多学科优化设计、喷雾燃烧等重点研究方向,承担了863、973、民用航天、国家自然科学基金及院所合作等一大批科研项目,发展迅速。目前年均科研经费近4000万元,年均发表高水平SCI论文50余篇,授权专利30项左右。研究获国家技术发明奖二等奖3项,三等奖1项;省部级科技进步一等奖3项,二等奖10项,其它部级科技奖近20项。

国家发明奖获奖证书
7、实验室建设
2012年5月位于新校区的宇航推进实验室和真空羽流实验室落成,总建筑面积超过6000平方米,最大层高超过15米。恢复和新建的实验台有液体火箭发动机实验台、涡轮泵实验台、喷雾燃烧实验台、固液火箭发动机实验台、超燃冲压发动机实验台、电推进实验台、微推进实验台、高温超导磁悬浮助推实验台、固体发动机性能实验台、固体推进剂燃速测试台、热防护实验台、结构振动试验台、点火技术实验台、姿轨控发动机实验台等。新的实验室及设备条件将有力保障未来宇航推进系的教学和科研发展。

宇航推进实验室 真空羽流效应试验系统
Department of Aerospace Propulsion
1、Overview
The Department of Aerospace Propulsion was descended from the former Department of Rocket Design and Rocket Engine which was founded in 1956. Thereafter, thediscipline and specialty of Liquid Rocket Engine Design and Solid Rocket Motor Design were established in 1958. And in the same year, Beijing-2, first modern sounding rocket in Asia, was successfully launched. The School of Astronautics was founded in 1988, and the department was renamed to Department of Aerospace Propulsion.
Currently, there are 42 faculties in the department, including13Professors/PhD supervisors and 24 associate professors. The discipline specialty has always been the first place in China. The annual enrollment is about 60 undergraduate students, 45 graduate students, 15 doctorial students, and several foreign students.
The department has the total construction area of approximately 6000m2 which includes the advanced aerospace propulsion laboratory and vacuum plumes laboratory and keeps long-term academic exchanges and scientific research collaboration with relevant departments and agencies in the United States, Russia, Europe, etc.
Research areas include liquid rocket engine, solid rocket motor, electric propulsion and other space propulsion. The main research directions are as follows: the rocket engine vacuum plumes, reusable liquid rocket engine multidisciplinary design optimization, full flowstaged combustion cycle engine, hybrid rocket motor, divert/attitude control solid rocket motor, aerospike nozzle, solid propellant combustion driven gasdynamic laser, arcjet engine, colloid micro-thrust engine, scramjet, spray and combustion technology, ignition technology, etc.

Gasdynamic laser test Earthquake rocket prize
2、History Evolution
The former department of rocket engine was established in 1956 and then in 1958, the rocket department was founded and the faculty of rocket engine was merged into the department. Two years later, the faculty of Liquid Rocket Engine Design and the faculty of Solid Rocket Motor Design were established. But in the year of 1970, these three faculties were merged into department of aircraft engine and formed a new faculty which was called faculty 403, the former name of Department of Aerospace Propulsion. On the base of the Rocket Department, BUAA established the School of Astronautics(SA) in 1988, the rocket engine faculty was re-merged into SA from the former department of aircraft engine. In 2006 according to requirement of the national major development, the rocket engine faculty was renamed to the current Department of Aerospace Propulsion.
3、Discipline Construction and Development
Department of Aerospace Propulsion belongs to the first level subject of Aerospace Science and technology, which was nation's earliest academic doctorate conferred in this first level subject. In the recently national evaluation in January 2007, the first level subject was identified as national key subject, and has been ranked first in China.The second level subject which Department of Aerospace Propulsion belonging to is Aerospace Propulsion Theories and Engineering. It has been identified as national key second level subject in 1988, also has been ranked place in the previous disciplines appraisal which was organized by the Ministry of National Education.As one of the first universities to enter the 2011 program, our department has hosted the construction of the Collaborative Innovation Center for Aerospace Science and Technology "Energy and Power Platform" of China and successfully completed the construction of the platform.The department which has doctorate or master's degree granting was conferred to construct the defense shortage second level subject "Electric propulsion technology" in 2007. Aerospace propulsion is a very comprehensive technical engineering subject, which involving machinery, combustion and flow, heat transfer, plasma physics, materials science, etc. Experiment, simulation calculation, optimization design, measurement and control, information processing, power supply, and many other related fields are involved in researches.
4、Education
The 4-year undergraduate professional name of the department is "aircraft propulsion engineering (space engineering)". Training objective is to cultivate high-level high-quality talent who has creative potential, team spirit and good at learning practice. Basic requirements: understanding necessary mathematics, physics and other natural science knowledge for the major; mastering engineering mechanics, mechanical design, mechanical manufacturing,electronics, computer application and other modern engineering and technical knowledge. The main specialized fundamental courses are engineering thermodynamics, engineering fluid mechanics, gas dynamics, heat transfer theory, etc. Main professional courses are Principle of rocket engine (including SRM principle, LRE principle, Principle of LRE propellant delivery system, Turbine pump principle), Design of rocket engine (including SRM design, LRE thrust chamber design, turbine pump design) and Rocket engine professional comprehensive experiment which is National and Beijing exquisite course. The characteristics of the subject ·is strongly comprehensive and engineering, and it is directly facing the design and testing of space propulsion products. Several experimental practice courses have been set including the production practice, the comprehensive experiment, professional curriculum design, professional comprehensive experiment, graduation design, etc. Student Research Training Program (SRTP) which is a high number of participants, big scale, high investment and long time program can significantly improve the students' cultivation quality, and it is received highly praise, such as successful launch of BEIHANG-1, BEIHANG-2, BEIHANG-3 etc. The department also havedeveloped acomplete, advanced and standard teaching laboratory and equipment conditions, including demonstration experiment, leading experiment and independent experiment. Top 3% undergraduate students may have opportunity to become PhD student without exam, and top 20% are able to be recommended to graduate students. Master's schooling is 2 years and 4 months, and top 20% grade one students have chance to do PhD students and top 30% grade two students may become to PhD students. PhD schooling is about three to eight years, which depends on the type of PhD and dissertation progress.

BEIHANG-3 in launching
5、Research Works
In recent years, aiming at the national great strategic demand and the international academic frontier, Department of Aerospace Propulsion has made rapid development around the rocket engine vacuum plumes, reusable rocket engine, hybrid rocket motor, attitude control rocket motor and power system, electric propulsion, scramjet, multidisciplinary design optimization, spray combustion and other key research direction. Department has undertaken a large number of scientific research projects, including 863, 973, National Natural Science Foundation and cooperation with many research institutes. At present, the annual average scientific research funds reach to nearly 40 million RMB. More than 50 SCI papers are published and about 30 national. The department has got 2 second prizes and 1 third prize of national technological invention, about 20 prizes of other ministry technology.
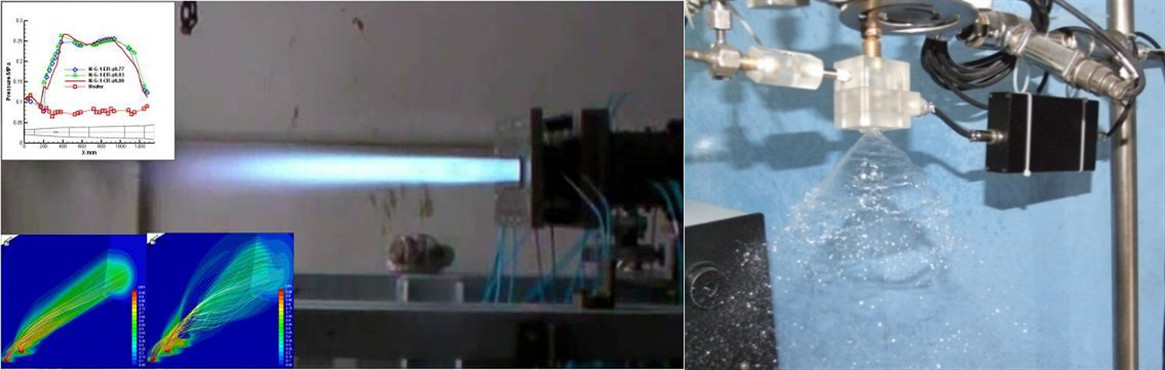
Scramjet testing LREPropellant atomization

Electric propulsion test Attitude and altitude control rocket

National invention prize certificates
6、Laboratory Construction
Aerospace propulsion laboratory and vacuum plume laboratory located in the new campus of Beihang University were built in May 2012, which have a more than 6000 square meters total construction area and more than 10 meters maximum height.Our department and the Institute of Beijing Aerospace Power Research of CASC jointly build "low-temperature liquid propulsion technology" Key Laboratory. Our department also actively participates in the construction of "Spacecraft Simulation Optimization and Dynamic Simulation" Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education. Several test platform will be restored and developed, including full flow staged combustion cycle engine test platform, aerospike nozzle test platform, scramjet test platform, arcjet test platform, high temperature superconductor bulk magnetic levitation and propulsion test platform, turbine pump test platform, GOX/alcohol LRE test platform, solid propellant combustion driven gasdynamiclaser test platform, spray and combustion test platform, SRM performance test platform,solid-propellant burn rate measurement platform, colloid micro-thrust engine test platform, thermal protection experiment platform, hybrid rocket motor test platform, gasdynamic resonance ignition experiment platform, detonation wave ignition experiment platform, pulse combustion experiment platform, insensitive firing cap experiment platform, divert/attitude control solid rocket motor test platform, etc. New laboratory and equipment will guarantee the needs of teaching, scientific research and development in the future.

Aerospace propulsion laboratory Vacuum plume laboratory